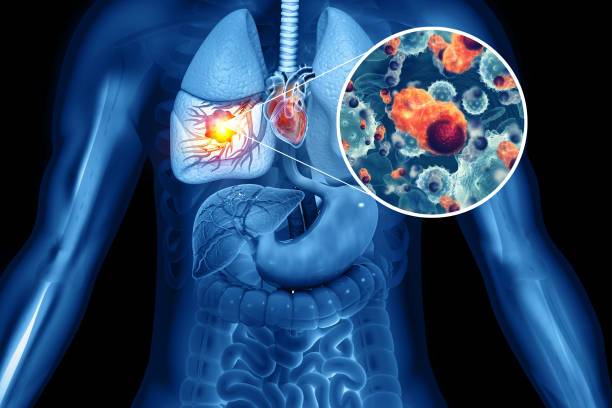
LUNG CANCER / 4 Stages/ Causes of lung cancer / Best Treatment
Know about Lung Cancer :
Lung Cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph bumps or other organs in the body, similar to the brain. When cancer cells spread from one organ to another, they’re called metastases.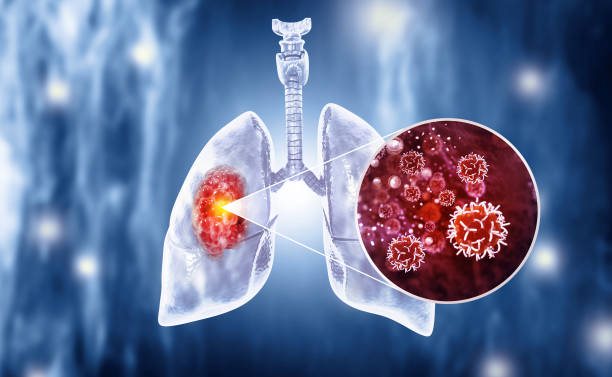
What are the 1st signs of lung cancer?
• Coughing that gets worse or does not go down.
• Casket pain.
• Briefness of breath.
• Wheezing.
• Coughing up blood.
• Feeling veritably tired all the time.
• Weight loss with no given cause.
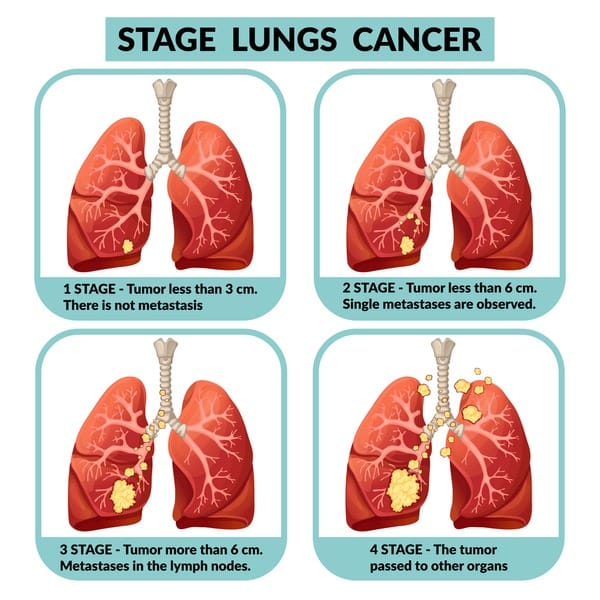
4 stages of lung cancer :
Like numerous other cancers, is frequently offered to describe the extent of the complaint and companion treatment opinions. The most generally used staging system for lung cancer is the TNM system, which stands for Tumor, Nodes, and Metastasis. This system divides lung cancer into four main stages.
Stage 1( I) of In this stage, the cancer is localized to the lung and has not spread to near lymph bumps or distant spots.
Stage 1A The excrescence is small and limited to the lung, without irruption of near structures.
Stage 1B The excrescence may be slightly larger or may involve the lung’s external covering( pleura), but it has not spread to lymph bumps or distant spots.
Stage 2( II) In stage 2, the cancer has generally grown larger or may have spread to near lymph bumps, but it’s still limited to the casket area.
Stage 2A The excrescence is larger and may have raided near structures or lymph bumps.
Stage 2B The excrescence may have raided near structures and may involve multiple lymph bumps.
Stage 3( III) Stage 3 lung cancer is considered locally advanced. It has generally spread to lymph bumps in the casket or near structures.
Stage 3A has spread to lymph bumps on the same side of the casket as the primary excrescence.
Stage 3B has spread to lymph bumps on the opposite side of the casket or to lymph bumps near the collarbone.
Stage 3C has spread to lymph bumps above the collarbone or lymph bumps on both sides of the casket.
Stage 4( IV) Stage 4 is considered advanced or metastatic. In this stage, the cancer has spread to distant corridors of the body, similar to other organs or bones. It’s frequently more grueling to treat at this stage.
- Each stage of lung cancer has specific treatment options and vaticinations. Beforehandstage lung cancer( Stage 1 and Stage 2) is frequently treated with surgery, while more advanced stages( Stage 3 and Stage 4) may bear a combination of treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation remedy, targeted remedy, immunotherapy, or palliative care to manage symptoms and ameliorate the quality of life.
- Staging is determined through a combination of imaging studies( similar to CT reviews and PET reviews), necropsies, and other individual tests. Individuals diagnosed with lung cancer need to work closely with their healthcare platoon to determine the most applicable treatment plan grounded on their specific stage and individual factors. Beforehand discovery and treatment can ameliorate the chances of a favorable outgrowth, so regular check-ups and lung cancer webbing for those at high threat are essential.
Is lung cancer severe?
The five-time survival rate for lung cancer is 56 percent for cases detected when the complaint is still localized( within the lungs). still, only 16 percent of cases are diagnosed at an early stage. For distant excrescences( spread to other organs) the five-time survival rate is only 5 percent.
Causes of lung cancer :
Lung cancer is primarily caused by exposure to threat factors, with tobacco bank being the leading cause. They are the primary causes and threat factors associated with lung cancer
1. Tobacco Bank Smoking is the single most significant threat factor for lung cancer. It’s estimated that over 85% of cases in the United States are caused by smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. The carcinogens(cancer-causing substances) in tobacco banks can damage lung cells and lead to the development of cancerous excrescences.
2. Secondary Bank Exposure to secondary banks, also known as unresistant banks or environmental tobacco banks, can increase the threat to nonsmokers. Breathing in the bank exhaled by smokers or the bank from burning tobacco products can be dangerous.
3. Radon Gas Radon is a naturally radioactive gas that can enter homes through the ground. Dragged exposure to high situations of radon is a significant threat factor, especially in areas with high radon situations.
4. Occupational Exposures Certain plant exposures to carcinogens can increase the threat. These exposures may include asbestos, arsenic, diesel exhaust, chromium, nickel, and colorful chemicals set up in some diligence.
5. Air Pollution Dragged exposure to high situations of air pollution, particularly in areas with poor air quality, may slightly increase the threat of lung cancer.
6. Family History A family history of lung cancer may indicate an inheritable predilection to the complaint. While the maturity of lung cancers isn’t inherited, a small chance may have an inheritable element.
7. Radiation Exposure to former radiation remedies to the casket area, especially during nonage, may increase the threat of developing lung cancer.
8. Lung conditions Certain lung conditions, similar to habitual obstructive pulmonary complaint( COPD) and pulmonary fibrosis, are associated with an advanced threat of lung cancer.
9. Salutary Factors A diet low in fruits and vegetables and high in red meat or reused flesh may be a minor threat factor for lung cancer. still, the part of the diet in lung cancer development isn’t as well-established as other threat factors.
10. Particular History Individualities who have preliminarily had lung cancer are at an increased threat of developing an alternate primary lung cancer.
Where does lung cancer start?
Generally starts in the cells lining the bronchi and corridor of the lung similar to the bronchioles or alveoli. A thin filling subcaste called the pleura surrounds the lungs. The pleura protects your lungs and helps them slide back and forth against the casket wall as they expand and contract during breathing.
Symptoms of lung cancer:
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of lung cancer, its position, stage, and other factors. Some people with lung cancer may not witness conspicuous symptoms in the early stages of the complaint. still, when symptoms do appear, they may include
1. Patient Cough A habitual cough that doesn’t go down or worsens over time is a common symptom of lung cancer. It may produce foam( mucus) that may be bloody or discolored.
2. Briefness of Breath Difficulty breathing or briefness of breath, especially with physical exertion, may do as the excrescence grows and affects lung function.
3. Chest Pain chest pain that’s constant or worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing can be a symptom of lung cancer. The pain may be sharp or dull and may be located in the chest, shoulder, or back.
4. Hoarseness A patient change in the voice, similar to hoarseness, may occur if the cancer affects the oral cords or near structures.
5. Gasping gasping or an effervescing sound when breathing can be due to airway inhibition by the excrescence.
6. Unexplained Weight Loss Unintentional weight loss, frequently accompanied by loss of appetite and muscle wasting, can be a sign of advanced lung cancer.
7. Fatigue Severe fatigue or a general feeling of weakness and frazzle may be endured, frequently without an egregious cause.
8. Coughing up Blood Hemoptysis, or coughing up blood or blood-barred foam, can be a concerning symptom of lung cancer.
9. Frequent Respiratory Infections Repeated or patient respiratory infections, similar to bronchitis or pneumonia, may occur as the vulnerable system is compromised.
10. lump of the Neck and Face lump of the face, neck, or upper extremities( superior vena cava pattern) may be affected by excrescence contraction of blood vessels.
11. Difficulty Swallowing Dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, can occur when an excrescence in the lung or esophagus presses on the swallowing tube( esophagus).
12. Bone Pain Bone pain, especially in the reverse, hips, or caricatures, may be a symptom of lung cancer that has spread to the bones( bone metastases).
13. Nail and Cutlet Clubbing Changes in the nails, similar to clubbing( blowup and rounding of the fingertips), may do in some cases. It’s important to note that these symptoms can be caused by many other medical conditions, and having one or further of these symptoms doesn’t inescapably mean you have lung cancer. still, if you or someone you know gets a patient or unusual respiratory symptoms or threat factors for lung cancer( similar to a smoking history), it’s essential to seek prompt medical evaluation by a healthcare provider.
Early discovery can lead to further effective treatment options and better outcomes. However, individual tests are similar to casket X-rays, and CT reviews, If suspected.
Treatment of lung cancer:
The treatment depends on several factors, including the type of lung cancer, its stage, the case’s overall health, and individual preferences. Treatment may involve one or a combination of the following approaches
1. Surgery Surgical junking of the excrescence is frequently recommended for early-stage.
- Lobectomy junking of one lobe of the lung
- Pneumonectomy junking of an entire lung
- Wedge resection junking of a small portion of the lung
- Segmentectomy junking of a larger portion of the lung than a wedge resection but not an entire lobe
1. Radiation Therapy Radiation remedy uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to target and kill cancer cells. It may be used before surgery(neoadjuvant), after surgery( adjuvant), or as the primary treatment for certain cases who can not suffer surgery.
2. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy involves the use of medicines to destroy or decelerate the growth of cancer cells. It may be used before or after surgery, in combination with radiation remedy, or as the primary treatment for advanced-stage lung cancer.
3. Targeted remedy Targeted remedy medicines are designed to target specific motes or pathways involved in cancer growth. They’re used for specific types of non-small cell lung cancer( NSCLC) that have specific inheritable mutations, similar to EGFR mutations or ALK rearrangements.
4. Immunotherapy Immunotherapy medicines work by stimulating the vulnerable system to fete and attack cancer cells. They’ve become an important treatment option for some cases with advanced stage, particularly those with high situations of PD- L1 expression.
5. Palliative Care Palliative care focuses on managing symptoms, relieving pain, and perfecting the quality of life for cases with lung cancer. It’s an essential element of care, especially for those with advanced-stage cancer.
6. Clinical Trials Participation in clinical trials may be an option for some cases, offering access to innovative treatments and curatives being studied for lung cancer.
7. Probative Care includes treatments and interventions to manage side goods of cancer treatment, similar to pain, nausea, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
The choice of treatment depends on the type of lung cancer and its stage. Treatment plans are personalized for each case and are generally developed by a multidisciplinary platoon of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, surgeons, radiation oncologists, and other specialists.
Cases need to have open and ongoing conversations with their healthcare platoon to make informed opinions about treatment options and pretensions of care. Beforehand discovery and treatment can lead to better issues, so regular check-ups and lung cancer webbing for high-threat individuals are essential. also, the smoking conclusion is pivotal to helping the development of lung cancer and ameliorating overall health.