ADDICTIVE BEHAVIOR : 4 EFFECTIVE ELEMENTS OF ADDICTIVE BEHAVIOR
WHA IS ADDICTIVE BEHAVIOR:
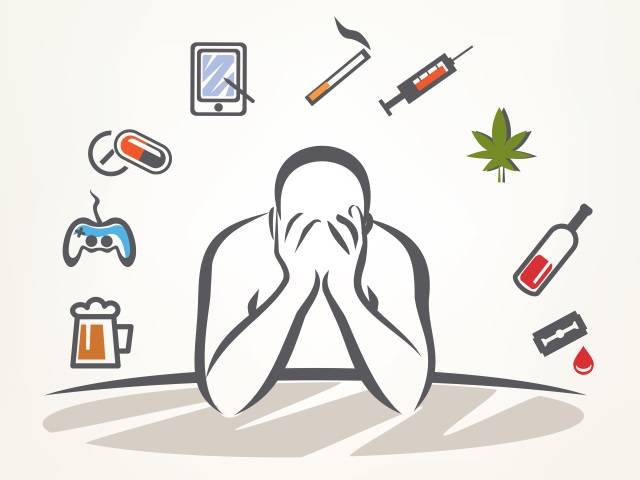
Addictive behavior refers to a pattern of actions characterized by a compulsive engagement in a particular activity, substance, or behavior, despite negative consequences. Individuals may find it challenging to control or stop the behavior, leading to a cycle of craving, indulgence, and temporary relief, followed by guilt or remorse. Common addictive behavior include substance abuse, gambling, excessive gaming, or overeating. Addiction often involves both physical and psychological components, with a significant impact on one’s daily life and overall well-being.
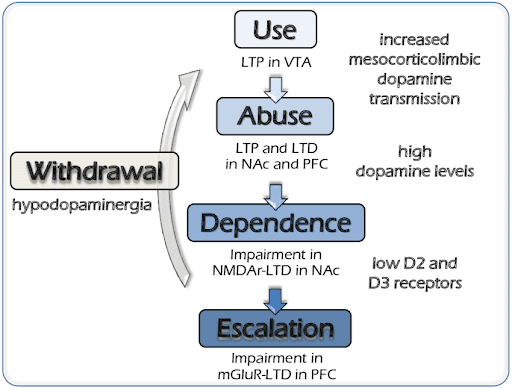
Behavioral Dependences- Dependence Center:
Although these are the most common types of behavioral dependencies (Addictive behavior), obsessive robbery( kleptomania), love and relationship dependence, overstepping, obsessive skin and hair selection, and excessive TV use and exercise are also listed as Addictive behavior.
What are the effects of addictive behavior:
Physical Health goods
Substance Abuse The abuse of substances like alcohol, medicines, and tobacco can lead to serious physical health issues, including organ damage, respiratory problems, cardiovascular conditions, and an increased threat of accidents are Addictive behavior thinkings.
Unhealthy Eating Addicting eating patterns can lead to rotundity, diabetes, heart complaints, and other metabolic diseases.
Increased threat of Mental diseases Addicting actions can contribute to or complicate internal health conditions like depression, anxiety, and bipolar complaint.
Bloodied Cognitive Function Substance abuse and certain addicting actions can vitiate cognitive functions similar to memory, attention, and decision-making
Social and Interpersonal goods
- Insulation Addicting actions can lead to social pullout and insulation as individuals prioritize their addicting habits over social relations.
- Strained connections The negative consequences of dependence, similar to lying, dishonesty, and erratic geste, can strain connections with family, musketeers, and associates.
Financial Consequences of Addictive Behavior
- Dependence can lead to fiscal insecurity due to spending plutocrats on substances, gambling, or other addicting conditioning, frequently at the expense of essential requirements.
Occupational Consequences of Addictive Behavior
- Dropped Performance Addicting actions can lead to dropped productivity and poor job performance, potentially resulting in job loss.
Legal Issues of Addictive Behavior
- Numerous addicting actions, similar to substance abuse and gambling, can lead to legal problems due to actions like driving under the influence or engaging in illegal conditioning to sustain the dependence.
Health and Safety of Addictive Behavior
- Bloodied Judgment Addictive behavior actions can vitiate an existent’s judgment, leading to parlous actions and potentially dangerous situations.
- Accidents and Injuries Under the influence of substances or engaging in addictive behavior, individuals may be more prone to accidents and injuries.
Forbearance and Withdrawal
- With repeated exposure, the body may develop a forbearance to Addictive behavior substances, leading individuals to consume larger quantities to achieve the same goods.
- When trying to stop the addicting geste, individualities may witness pullout symptoms, which can be uncomfortable and distressing.
Loss of Control due to Addictive behavior
- Addictive behavior frequently lead to a loss of control, where individualities find it delicate to moderate or stop their engagement in the game despite negative consequences.
What are the 4 elements of addicting geste:
Addictive behavior generally partake four crucial rudiments, frequently appertained to as the” four rudiments of dependence .” These rudiments help to understand and define the nature of addicting actions.
- Coercion or pining This element refers to the violent appetite or desire an individual feels to engage in the addicting geste or consume the addicting substance. This pining can be both cerebral and physiological, and it frequently drives the person to engage in the geste despite negative consequences constantly.
- Loss of Control Individualities floundering with Addictive behavior frequently find it delicate to control or moderate their engagement in the geste. This loss of control is a hallmark of dependence, as the person continues to engage in the geste indeed when they had originally intended not to or when they’re apprehensive of the negative consequences.
- Negative Consequences Addictive behavior generally lead to negative consequences in colorful aspects of an existent’s life, similar to physical health, internal well-being, connections, work, and finances. Despite being apprehensive of these negative consequences, individuals with dependence frequently continue their geste due to coercion and loss of control.
- Escalation Over time, Addictive behavior frequently escalate in terms of frequency, intensity, or duration. This escalation is a result of the development of forbearance, where the individual requires larger quantities of the substance or further frequent engagement in the geste to achieve the said goods. Escalation can lead to a cycle of adding negative consequences and can make it harder to break free from the dependence.
These four rudiments are interrelated and contribute to the cycle of dependence. Addictive behavior help to explain why individuals find it so grueling to overcome addicting actions and why these actions can have such a significant impact on their lives. It’s important to fete these rudiments and seek applicable help and support if you or someone you know is floundering with addicting actions.
What are the characteristics of addicting geste:

- Coercion and pining individualities with Addictive behavior frequently witness strong urges or jones to consume the substance. This coercion can be difficult to repel, indeed when the person is apprehensive of the negative consequences.
- Loss of Control Addictive behavior is marked by an incapability to control the frequency or intensity of the geste. Individuals may have intentions to cut down or quit, but they find it challenging to do so.
- Neglect of liabilities As dependence takes hold, individuals might start neglecting their liabilities at work, academy, or home. Precedences shift as the Addictive behavior becomes the central focus.
- Negative Consequences Addictive behavior leads to adverse goods on physical health, internal well-being, connections, finances, and overall quality of life. Despite these negative issues, individuals continue engaging in the game.
What are the signs of addicting geste:
Feting the signs of addicting geste is pivotal in relating when someone might be floundering with a dependence. These signs can vary depending on the specific geste ( substance abuse, gambling, gaming, etc.), but then are some common signs to watch out for.
- Loss of Control The person is unfit to limit or control their engagement in the game, frequently engaging in it for longer ages or in larger amounts than intended.
- Obsession They spend a significant quantum of time allowing about, planning, or engaging in the geste, frequently to the detriment of other conditioning or liabilities.
- Neglecting liabilities They start neglecting their liabilities at work, academy, or home, as the guest takes priority.
- Withdrawal When trying to cut back or quit the geste, they witness physical or cerebral pullout symptoms similar to perversity, restlessness, anxiety, or indeed physical pain.
- Tolerance Over time, they need to engage in the geste more constantly or with lesser intensity to achieve the asked effect.
- Failed Attempts to Quit They make repeated attempts to quit or cut back on the game but are unprofitable or experience only short-term success.
- Continued Use Despite Consequences They continue engaging in the geste indeed when it’s causing negative consequences in their life, similar to health problems, relationship issues, or fiscal troubles.
- Loss of Interest They lose interest in conditioning they preliminarily enjoyed because the addicting geste has become the primary source of pleasure and price.
- Secrecy and Deception They hide their geste from musketeers, family, or associates and may lie about the extent of their involvement.
- Changes in Behavior There are conspicuous changes in their geste, mood, or personality. They might become more perverse, anxious, or withdrawn.
- Social insulation They withdraw from social conditioning, pursuits, and relations in favor of engaging in the addicting geste.
- Fiscal Problems They witness fiscal difficulties due to spending plutocrats on the geste, frequently neglecting essential requirements.
- Relationship Strain Their connections with family, musketeers, or mates come strained due to the geste and the associated deception and neglect.
- Mood Swings They parade mood swings, ranging from swooning when engaging in the geste to depression or perversity when not suitable.
- Escalation Over time, they escalate the geste by engaging in it more constantly or by seeking out more potent forms of the geste
How does dependence affect the brain?
Medicines or alcohol can commandeer the pleasure/ price circuits in your brain and hook you into wanting further and further. Dependence can also shoot your emotional peril- seeing circuits into overdrive, making you feel anxious and stressed when you are not using medicines or alcohol.
What does dependence mean in psychology:
Feting the signs of addicting geste is pivotal in relating when someone might be floundering with a dependence. These signs can vary depending on the specific geste ( substance abuse, gambling, gaming, etc.), but then are some common signs to watch out for.
- Loss of Control The person is unfit to limit or control their engagement in the game frequently engaging in it for longer ages or in larger amounts than intended.
- Obsession They spend a significant quantum of time allowing about, planning, or engaging in the geste, frequently to the detriment of other conditioning or liabilities.
- Neglecting liabilities They start neglecting their liabilities at work, academy, or home, as the guest takes priority.
- Withdrawal When trying to cut back or quit the geste, they witness physical or cerebral pullout symptoms similar to perversity, restlessness, anxiety, or indeed physical pain.
- Tolerance Over time, they need to engage in the geste more constantly or with lesser intensity to achieve the asked effect.
- Failed Attempts to Quit They make repeated attempts to quit or cut back on the game but are unprofitable or experience only short-term success.
- Continued Use Despite Consequences They continue engaging in the geste indeed when it’s causing negative consequences in their life, similar to health problems, relationship issues, or fiscal troubles.
- Loss of Interest They lose interest in conditioning they preliminarily enjoyed because the addicting geste has become the primary source of pleasure and price.
- Secrecy and Deception They hide their geste from musketeers, family, or associates and may lie about the extent of their involvement.
- Changes in Behavior There are conspicuous changes in their geste, mood, or personality. They might become more perverse, anxious, or withdrawn.
- Social insulation They withdraw from social conditioning, pursuits, and relations in favor of engaging in the addicting geste.
- Fiscal Problems They witness fiscal difficulties due to spending plutocrats on the geste, frequently neglecting essential requirements.
- Relationship Strain Their connections with family, musketeers, or mates come strained due to the geste and the associated deception and neglect.
- Mood Swings They parade mood swings, ranging from swooning when engaging in the geste to depression or perversity when not suitable to.
- Escalation Over time, they escalate the geste by engaging in it more constantly or by seeking out more potent forms of the geste.
- Guard They come protective or agitated when brazened about their behavior or when someone expresses concern.
It’s important to approach individualities with compassion and understanding. However, encourage them to seek professional help, similar to remedy, If you suspect someone is floundering with addicting behavior. Beforehand intervention can greatly ameliorate the chances of recovery and help the behavior from causing further detriment.
What does mean in psychology :
In psychology, dependence is defined as a complex and habitual brain complaint characterized by an obsessive engagement in satisfying stimulants despite adverse consequences. It involves a patient pattern of seeking and using a substance or engaging in a behavior, indeed when it has negative goods on an existent’s physical, internal, social, or emotional well-being.
- Dependence is considered a multifaceted condition that involves both cerebral and physiological factors. It frequently develops gradationally as a result of colorful factors, including inheritable predilection, environmental influences, neurobiological changes, and cerebral vulnerabilities.
- Coercion individuals with dependence experience strong Jones and force them to engage in the addicting behavior and consume the addicting substance. This coercion can be grueling to control and can stamp rational decisions- timber.
- Loss of Control One of the central features of dependence is the incapability to constantly control or moderate the behavior. People may want to quit or cut down, but they struggle to do so due to the important pull of the dependence.
- Negative Consequences Despite being apprehensive of the negative consequences, individuals with dependence continue to engage in geste or substance use. These negative consequences can include health issues, relationship problems, legal troubles, and more.
- Forbearance With repeated exposure to a substance or geste, the existent may develop a forbearance, which means that over time, they bear larger quantities or further violent engagement to achieve the asked goods.
- Withdrawal When the addicting geste or substance use is suddenly reduced or stopped, individuals may witness pullout symptoms. These symptoms can be physical, emotional, and cerebral and frequently contribute to the cycle of dependence.
- Hindrance with Daily Life Addiction can significantly disrupt an existent’s diurnal life, including their liabilities, connections, work, and overall well-being. The pursuit of the addicting geste becomes a primary focus.
- Escalation Over time, dependence frequently leads to an escalation in the geste. This can involve increased frequency, duration, or intensity of engagement, as individualities seek to maintain the asked goods.
- Pining Pining refers to the violent desire or prompt to engage in the addicting geste or use the substance. jones can be touched off by cues or monuments associated with the geste.
It’s important to understand that dependence is a complex condition that can affect people in colorful ways. Different substances and actions can lead to addicting actions, including substances like medicines and alcohol, as well as actions like gambling, gaming, and gluttony. Treatment and intervention for dependence frequently involve a combination of medical, cerebral, and social approaches to address the underpinning causes and help individuals manage and overcome their addicting actions.





